![]()
![]()
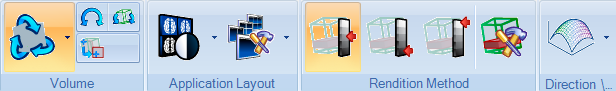
The following tab is added to the toolbar when you open the MPR application.
|
Icon |
Description |
|
Volume |
|
|
|
Swivel the image. |
|
|
Roll the image from side to side around the center of the volume. |
|
|
Roll the image to the closest axial, sagittal or coronal plane. |
|
|
|
|
Application Layout |
|
|
|
Duplicate a group of result images to manipulate them individually.
|
|
|
Select group layout:
You can also apply:
|
|
Rendition Method |
|
|
|
MPR (average MipPR) - Render the MPR slab using the average pixel value. |
|
|
MIP (maximum intensity projection) - Render the MPR slab using the maximum pixel value. |
|
|
MinPR (minimum intensity projection)- Render the MPR slab using the minimum pixel value. |
|
|
Control rendering parameters. Select rendition type, slice thickness and slice spacing. |
|
Direction |
|
|
|
Reformat plane and curve:
|